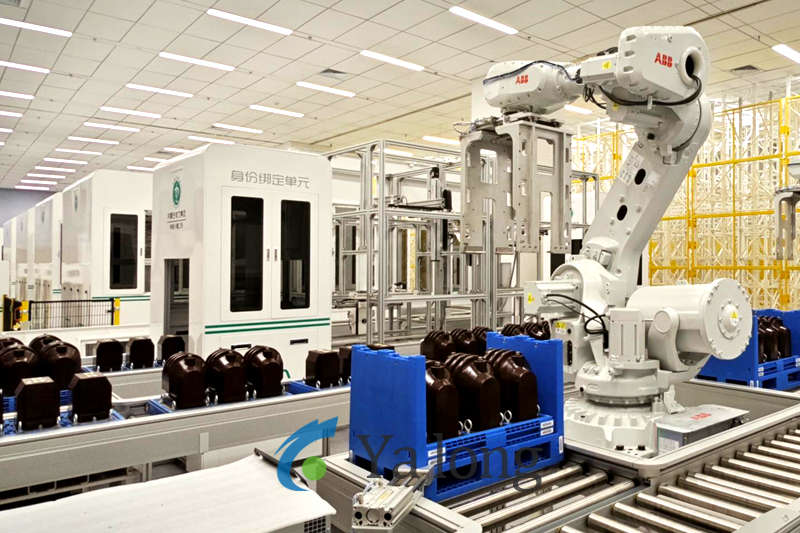
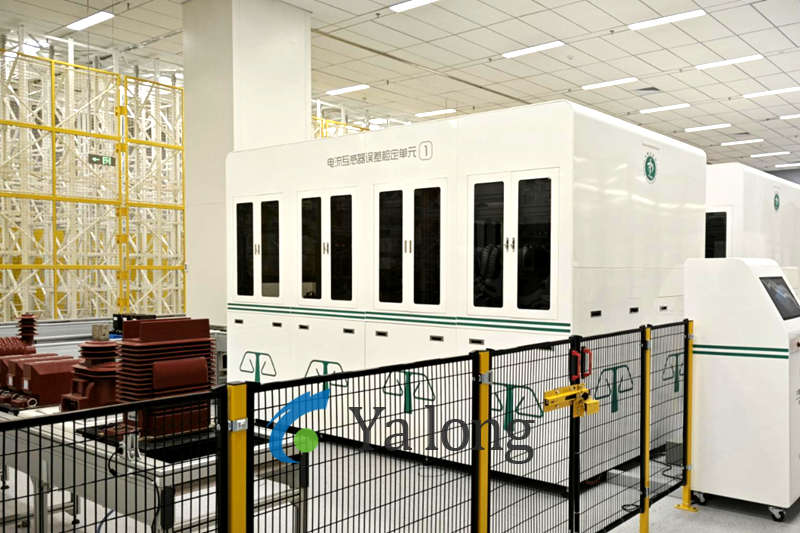
Current Transformer (CT) Assembly Line Technical Features
Core Process Characteristics
1.
Automation & Standardization
•
Winding tension: ≤±0.1N precision control
•
Curing temperature: ±2℃ tolerance
•
Robotic/CNC Integration: Applied in critical processes (winding, potting, testing)
•
Unified Tooling & Parameters:
•
Batch consistency: ≤0.5% variance
2.
Online Quality Traceability
•
Core annealing time/temperature logs
•
Test data (ratio error/phase displacement)
•
Unique QR Code Binding: Tracks full-process data
•
MES System Integration: Real-time data mapping for lifecycle traceability
3.
Flexible Adaptation
•
Capacity: 10A–5000A
•
Accuracy: Class 0.2S to Class 1
•
Winding turns: 50–2000 turns programmable
•
Mold size: 20+ modular fixtures
•
Rapid Changeover: ≤10-min specification switching via parameter adjustment
•
Multi-spec Compatibility: