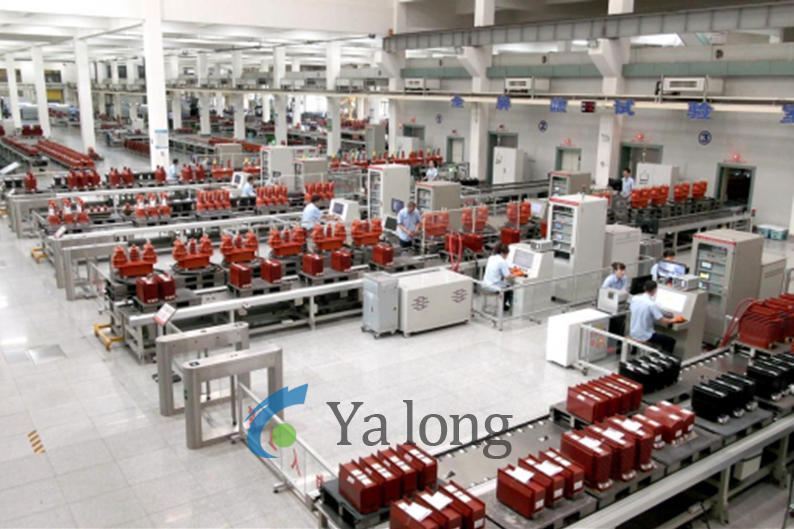
Voltage Transformer (VT) Assembly Line Technical Specification
Core Components & Technologies
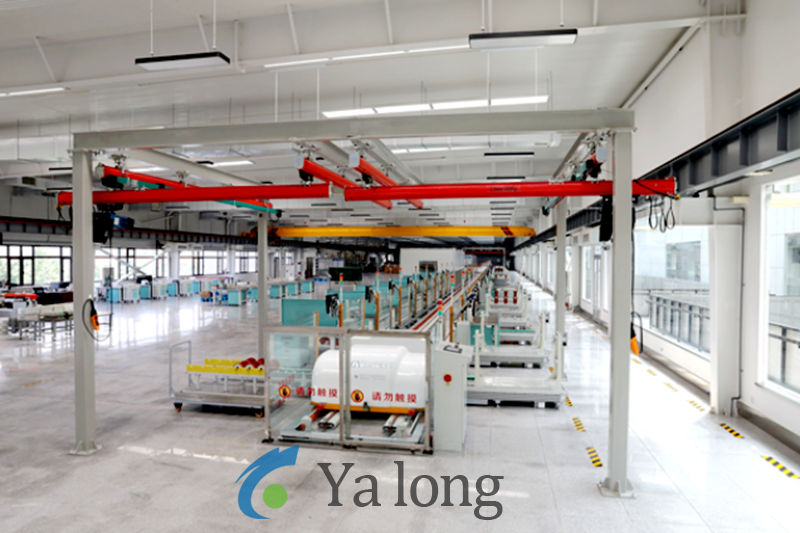
1. Conveying System
•
Precision Roller Conveyor/Dual-Speed Chain Conveyor
•
Positioning Tooling:
•
Mechanical limiters + vacuum adsorption
•
Workpiece positioning accuracy: ±0.1mm
2. Automated Winding Technology
•
Fully Automatic CNC Winding Machine:
•
Winding tension control (prevent breakage/slack)
•
Turn count error: ≤±1 turn
•
Servo motor + precision wire spreader
•
Wire types: Copper/Aluminum enameled wire
•
Real-time Monitoring:
•
Auto-binding of winding endpoints
3. Modular Adaptation System
•
Rapid Switch Tooling:
•
Supports 10kV/35kV/110kV voltage levels
•
Compatible with oil-immersed/dry-type structures
•
Program-Driven Parameter Switching:
•
Primary winding: Thick wire, few turns (e.g., 110kV: Ø2.0mm, ≤50 turns)
•
Secondary winding: Thin wire, multiple turns (e.g., 100V output: Ø0.5mm, 500+ turns)